Vibration Acceptance Testing Avoided Long Term Reliability Issues
Lowered the risk of vibration problems at commissioning and over the life of the plant with a properly specified and performed acceptance test including an experimental modal analysis (impact) test.
Motion Magnified Video is a good tool for seeing potential rotating machinery system issues, such as, soft foot, piping support problems, foundation cracks, etc. This magnified video shows excessive system motion when the pump is operated below it's specified minimum operating speed. Vibration was acceptable within the specified running speed range (70% to 100% of maximum running speed).
1. Problem Statement (Challenge)
- What (type of machine): Single stage double suction vertically mounted split case driven by 300HP motors through a long line shaft in low lift service.
- Where (State/Country): Upper Midwest, United States
- Why (problem/reason): Provided post-installation vibration testing services after a new motor and VFD were installed. The concern was converting the pumps from constant speed to variable speed while also adding new motors with different mass can introduce a resonance (high vibration) issue at start up or over the life of the plant.
- Acceptance criteria: ANSI/Hydraulic Institute (HI) 9.6.4 plus ISO 10816-3 for the motor vibration measurements along with confirming that specified natural frequency separation margins were met.
2. Work Performed
Methods:
- Triaxial accelerometers were temporarily installed per ANSI/HI 9.6.4 and ISO 10816-3.
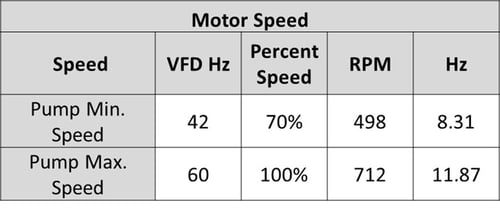
- Experimental Modal Analysis (EMA, impact) testing was properly performed. The natural frequencies of each structure (motor, driveshaft, and pump) plotted as a Frequency Response Function (FRF) were compared to potential pump excitations to evaluate separation margin (potential resonance).
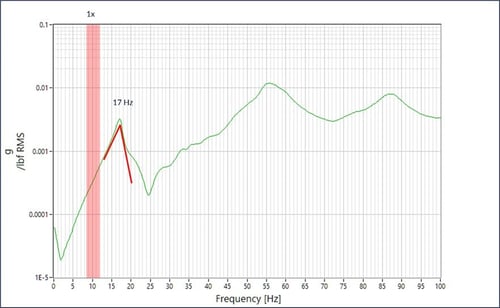
- Operational testing was performed on the pump system through a speed range of 70%-100%. This vibration data was collected for approximately 1-hour and displayed as an overall vibration trend compared to the HI spec for this pump type as well as the ISO spec for this motor mounting type.
- Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) plots were evaluated for potential issues, such as, imbalance, misalignment, bearing defects, and rubbing while the pump was operating within the running speed range.
- VibVue® Motion Magnification Video (MMV) testing was performed while the pump system was operating, amplifying the motion of the pump system so that the main excitations can be seen by the human eye.
- Vibration data for the non-operating pump(s) were also recorded for sympathetic vibration as required by ANSI/HI 9.6.4.
- A plant flow meter was used to determine where the pump is operating on its curve during the vibration acceptance test (Allowable Operating Region or AOR, Preferred Operating Region or POR, or outside the AOR).
3. Results/Solution
Findings:
- The pumps and motors had acceptable vibration within the running speed range:
- Overall vibration limits set by HI 9.6.4 for a 300 HP system should not exceed 0.19 in/s RMS while running in the POR.
- Motor vibration limits set by ISO 10816-3 should not exceed 0.177 in/s RMS in its allowable running range.
- Separation margin criteria was less than 10% indicating that a potential resonance (high vibration) issue was possible or even likely during the plant operating life. Separation margin was achieved after mass was correctly added to the motor.
MSI’s VibVue® MMV test results show acceptable motion within the running speed range but high motion when operating just outside of the running speed range (acceptable with added motor mass).
Impact:
- MSI recommended accepting the pump system from a vibration standpoint for operation within the 70% to 100% speed (498 rpm to 712 rpm) with or without the added motor mass.
- The specified natural frequency separation margins were only met with the added motor mass.
- The probability of avoiding high vibration issues due to resonance over the plant operating life was significantly increased with the MSI recommended motor mass addition.
Summary of running speed range: The pumps were converted from constant speed to variable speed which can lead to exciting previously benign natural frequencies. New motors with different dynamic characteristics including mass were also changing the system natural frequencies.
One example FRF plot from among many resulting from a properly specified and performed Experimental Modal Analysis (EMA, impact) test. This example shows acceptable separation margin from running speed. This means, high vibration due to resonance is unlikely at commissioning and over the plant operating life. Other FRFs indicted a separation margin issue.
Overall vibration data showing that the pumps fall within the ANSI/HI specified vibration criteria at this measurement location in the vertical (blue), perpendicular (red) and parallel (green) directions relative to the pump discharge flange.
REAL-WORLD EXAMPLES AND CASE STUDIES
MSI In Action
Case Study
Design, Analyze, and Build a Prototype Radial Gas Turbine
MSI was tasked with designing a prototype 20 hp high speed radial gas turbine generator to operate at 40,000 RPM with R-134a as the working fluid.
Case Study
Design of Oil Extraction Gear Pump & Motor
MSI was contracted to design a down-hole, multi-set external gear hydraulic motor – pump unit.
Case Study
Axial Hydro Turbine Design and Test
MSI was tasked with designing a subscale (1/6th) axial hydro-turbine utilizing a belt system to drive a generator.
